Better LLM Prompts Using XML
This article explains why using XML solves some problems with prompting and provides better results from an LLM.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing, but crafting effective prompts can be challenging. Unstructured prompts often lead to inconsistent results. Enter XML-structured prompts. XML-structured prompts enhance LLM interactions by improving clarity, accuracy, and parsability of AI responses. This concept is even more critical when using smaller models.
Until recently, I’ve been asking LLM’s questions about writing code, or open ended questions to expand on ideas for chapter content. Large LLM’s such as Claude and ChatGPT are great for this purpose.
When I starting diving into using smaller locally-run LLM’s for parsing pentest scan data, I found that it’s critical to use carefully designed prompts with them. That’s when I read about using XML to design LLM prompts. Incorporating well-structured and defined XML prompts into my AI projects has been crucial for getting the best results.
The XML Advantage
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) offers several benefits when structuring LLM prompts:
Clear Delineation: XML tags provide distinct boundaries between different components of a prompt, reducing ambiguity.
Hierarchical Organization: Nested tags allow for logical grouping of related information.
Improved Parsing: XML-structured responses are easier to process programmatically.
Consistency: Standardized tags promote uniformity across different prompts and projects.
Flexibility: XML schemas can be easily modified or extended to accommodate new requirements.
Let’s explore two practical examples of XML-structured prompts to illustrate these benefits.
Example 1: Python Code Generation Prompt
Here’s an example of how to structure a prompt for generating Python code:
<prompt>
<task>Generate Python code</task>
<description>Create a function that calculates the Fibonacci sequence up to a given number</description>
<requirements>
<item>Use recursion</item>
<item>Include type hints</item>
<item>Add docstring with examples</item>
</requirements>
<output_format>
<language>python</language>
<version>3.9+</version>
</output_format>
</prompt>
This structured prompt clearly defines the task, specific requirements, and desired output format. The LLM can now generate a more accurate and tailored response based on these well-defined parameters.
Example 2: Cybersecurity Analysis Prompt
For cybersecurity engineers, here’s an example of a prompt structure for analyzing potential vulnerabilities:
<prompt>
<task>Vulnerability analysis</task>
<target_system>
<name>E-commerce web application</name>
<technology_stack>
<frontend>React</frontend>
<backend>Node.js</backend>
<database>MongoDB</database>
</technology_stack>
</target_system>
<focus_areas>
<item>SQL injection</item>
<item>Cross-site scripting (XSS)</item>
<item>Authentication bypass</item>
</focus_areas>
<output_format>
<structure>
<section>Vulnerability description</section>
<section>Potential impact</section>
<section>Recommended mitigation steps</section>
</structure>
<priority_scale>
<low>1-3</low>
<medium>4-7</medium>
<high>8-10</high>
</priority_scale>
</output_format>
</prompt>
This prompt provides a comprehensive structure for analyzing vulnerabilities in a specific system. It clearly defines the target, areas of focus, and desired output format, enabling the LLM to generate a more focused and actionable security analysis.
Implementation
Save the following Bash script as generate_prompt.sh:
#!/bin/bash
# Colors for better readability
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
BLUE='\033[0;34m'
NC='\033[0m'
echo -e "${BLUE}AI Prompt Generator${NC}"
echo "This script will help you create a structured XML prompt."
# Gather basic information
read -p "What is the main task or question for the AI? " main_task
read -p "What is your role or profession? " user_role
read -p "What is your location? " location
read -p "What is your preferred language? " language
# Get context details
echo -e "\n${GREEN}Context Information${NC}"
read -p "Are there any specific restrictions or limitations? " restrictions
read -p "Do you need specific formatting in the response? " formatting
# Get additional requirements
echo -e "\n${GREEN}Output Requirements${NC}"
read -p "What style should the response be in? (e.g., technical, casual, academic) " style
read -p "Should the AI include specific types of content? (e.g., code, math, diagrams) " content_types
# Generate XML prompt
cat << EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ai_prompt>
<task>$main_task</task>
<user_profile>
<role>$user_role</role>
<location>$location</location>
<language>$language</language>
</user_profile>
<requirements>
<style>$style</style>
<content_types>$content_types</content_types>
<formatting>$formatting</formatting>
</requirements>
<restrictions>$restrictions</restrictions>
</ai_prompt>
EOF
Make it executable with the command chmod +x generate_prompt.sh
Run it with the command ./generate_prompt.sh
The generated XML structure helps AI models better understand the context and requirements of your request, potentially leading to more accurate and relevant responses.
I’ll provide an example showing how I used the script output to create a better prompt I can use for one of my common pentesting taks that I frequently delegate to AI. Here’s the script output:
$ ./generate_prompt.sh
AI Prompt Generator
This script will help you create a structured XML prompt.
What is the main task or question for the AI? Create Frida JavaScript scripts for mobile application security testing.
What is your role or profession? Security Consultant and penetration tester
What is your location? United States
What is your preferred language? English
Context Information
Are there any specific restrictions or limitations? Ensure that you carefully evaluate the platform, Android or iOS from the user prompt, to ensure that you use the correct Frida API when creating scripts.
Do you need specific formatting in the response? The response should contain only JavaScript with proper formatting, and should be output in Markdown code block. No commentary should be provided. If you don't have enough information from the human, stop and ask any necessary questions.
Output Requirements
What style should the response be in? (e.g., technical, casual, academic) technical
Should the AI include specific types of content? (e.g., code, math, diagrams) code in JavaScript
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ai_prompt>
<task>Create Frida JavaScript scripts for mobile application security testing.</task>
<user_profile>
<role>Security Consultant and penetration tester</role>
<location>United States</location>
<language>English</language>
</user_profile>
<requirements>
<style>technical</style>
<content_types>code in JavaScript</content_types>
<formatting>The response should contain only JavaScript with proper formatting, and should be output in Markdown code block. No commentary should be provided. If you don't have enough information from the human, stop and ask any necessary questions.</formatting>
</requirements>
<restrictions>Ensure that you carefully evaluate the platform, Android or iOS from the user prompt, to ensure that you use the correct Frida API when creating scripts.</restrictions>
</ai_prompt>
I placed the XML content into a Claude.ai project instructions, as shown here:

Here’s the conversation where I used it to help me create a Frida script that helps me audit crypto ciphers during a mobile application pentest:
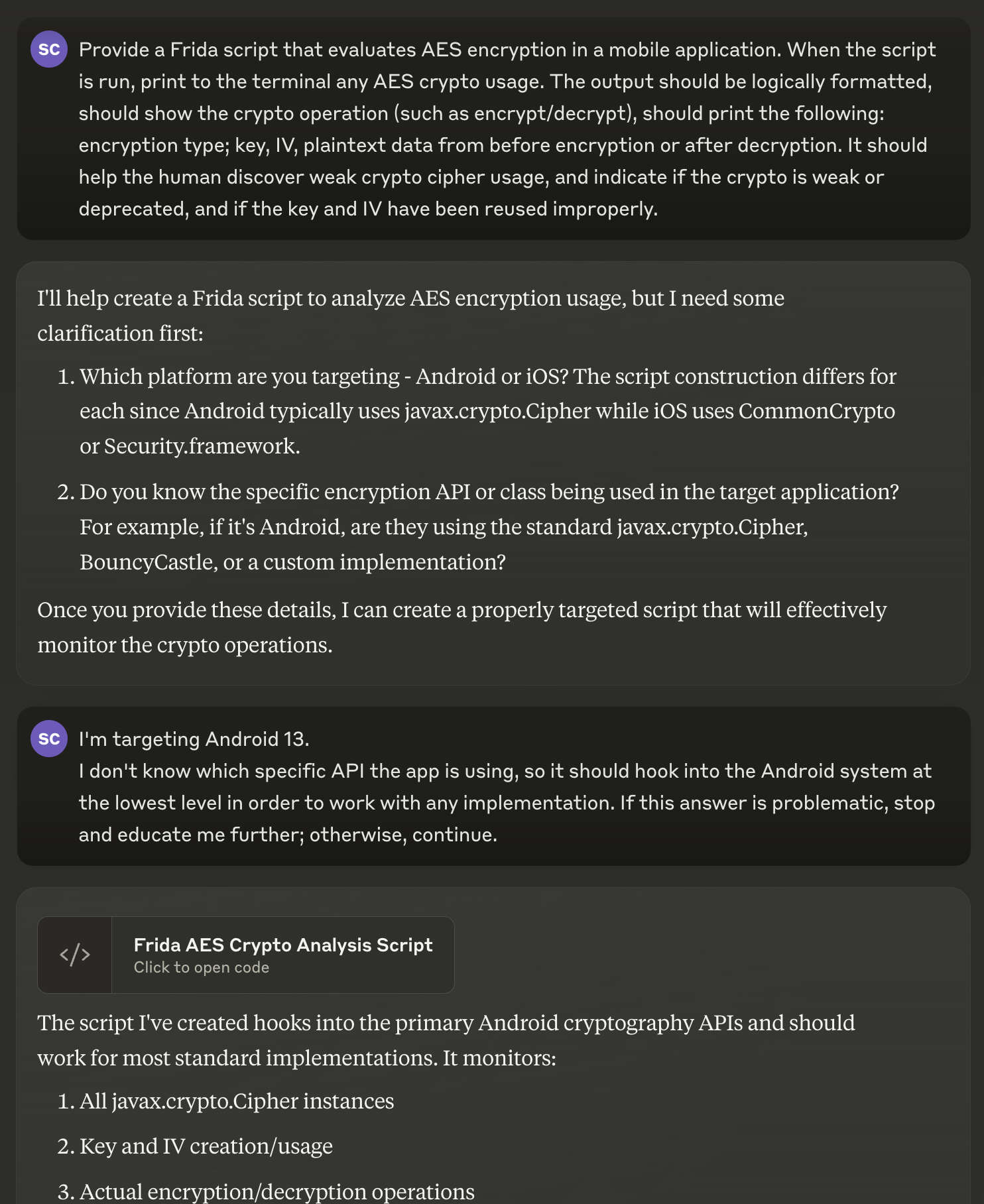
You can see how in the conversation, instead of making assumptions and providing bad output, it heeded my “system” instructions and asked for more guidance before providing the proper output. From my experience, if you simply tell AI what you want without putting significant thought and effort into your prompt, you won’t be happy with the results and you’ll think “AI sucks”. However, the problem frequently isn’t the fault of AI, it’s caused by your lack of knowledge of how to use it properly.
Best Practices
- Tag Selection: Use intuitive tag names that clearly describe their content. Common tags include:
<instructions>
<context>
<example>
<formatting>
<requirements>
- Consistency: Maintain the same tag structure throughout your conversation with the AI. This helps the model understand and maintain context across multiple interactions.
- Nesting: Organize complex prompts using nested tags to create clear hierarchies of information. This is particularly useful when dealing with multi-step tasks or detailed requirements.
- The use of XML tags helps AI models parse your prompts more accurately, leading to higher-quality outputs and more consistent responses. Whether you’re using the web interface or API, this structured approach can significantly improve your AI interactions.
Conclusion
By adopting XML-structured prompts, developers and cybersecurity professionals can reach the full potential of LLMs, obtaining more precise, consistent, and easily parseable responses. This approach not only enhances the quality of AI-generated content but also streamlines the integration of LLM outputs into existing workflows and applications[1][4].
As the field of prompt engineering continues to evolve, XML-structured prompts will become a standard practice, offering a foundation for more sophisticated and reliable AI-driven solutions[2][3].
Citations:
[1] https://xmlaficionado.com/XML+Aficionado/2024/04/Using+XML+Schema+in+AI+System+Prompts
[2] https://www.reddit.com/r/LocalLLaMA/comments/1dsuzn8/finetuning_a_llm_on_xml_files/
[3] https://github.com/Bradybry/chatXML
[4] https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/build-with-claude/prompt-engineering/use-xml-tags
